Cyber Threat Intelligence
At NetSpyre, our Cyber Threat Intelligence services are tailored to provide robust protection for your business digital landscape. We focus on mainly on leaked database research and analysis.
In today’s digital age, cyber threats have become a pressing concern for all, with businesses facing significant risks. We’re increasingly witnessing sophisticated cyber attacks that jeopardize confidential data, disrupt business operations, and tarnish corporate reputations.
A notable threat escalating in prevalence and impact is credential stuffing. This type of attack is alarmingly straightforward to carry out and can be highly effective. Its success largely stems from a common user practice: reusing identical passwords across various accounts.
Studies reveal that a staggering 85% of individuals reuse their passwords on multiple platforms. Such password habits significantly contribute to the success of credential stuffing attacks. It’s crucial for businesses to understand this threat and implement strategies to defend themselves, their customers, and their brand image. This article aims to demystify credential stuffing, explore its implications for businesses, and highlight key preventative measures to ensure security.
Understanding Credential Stuffing
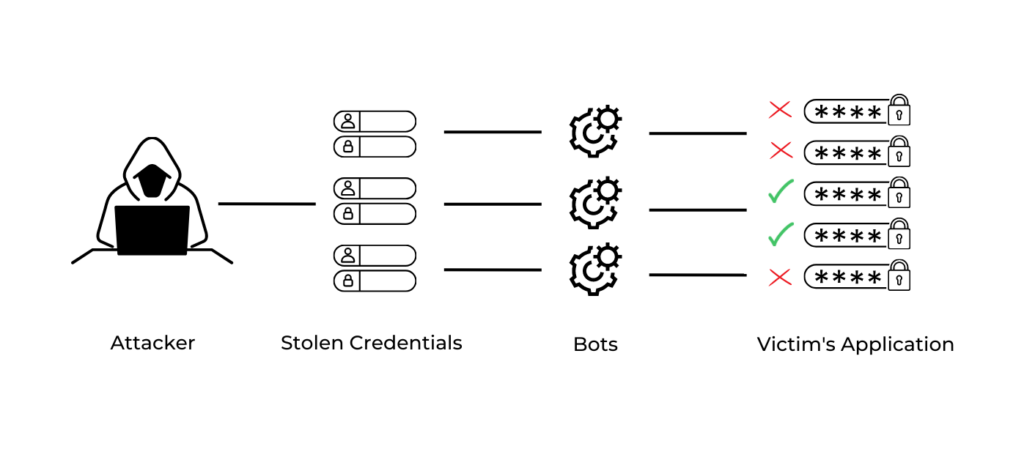
Credential stuffing is a cyber attack method where attackers use stolen username/email and password combinations to breach user accounts across different applications.
Typically, attackers acquire these credentials from data breaches or purchase them on the dark web. They then employ automated tools to test these stolen credentials on various applications, seeking unauthorized access to accounts.
Differentiating Credential Stuffing, Password Spraying, and Brute Force Attacks
It’s crucial for businesses to recognize the distinctions among credential stuffing, password spraying, and brute force attacks as they all aim to illicitly access sensitive information:
Credential Stuffing:
– Involves using pre-stolen credential lists to access accounts.
– Employs automated bots for account access attempts.
– Particularly successful against accounts with reused or weak passwords.
– Utilizes credentials (usernames/emails and passwords) from past data breaches.
Password Spraying:
– Tries to breach accounts by testing a few common passwords against numerous accounts.
– Aims to evade detection with limited attempts per account.
– Often successful with accounts secured by weak or commonly used passwords.
– Attackers use lists of usernames/emails and widely used passwords.
Brute Force Attack:
– Systematically attempts every possible character combination to access accounts.
– May use dictionary words, phrases, or random character combinations.
– Potentially effective against accounts with weak passwords.
– Attackers deploy specialized tools for these attacks, with time taken to crack passwords varying based on password complexity.
Credential stuffing represents a growing concern in the realm of cyber threats, particularly for its method of exploiting stolen username and password combinations. This attack aims to breach multiple accounts or services, often with alarming success.
Let’s break down a typical credential stuffing attack into its three key stages:
1. Acquisition of Stolen Credentials:
– The initial step for the attacker is to gather a list of compromised usernames or email addresses and passwords. These are usually sourced from past data breaches or purchased from the dark web.
2. Execution of Automated Attacks:
– Next, the attacker employs automated tools or bots. These bots rapidly test the stolen credentials across various applications, attempting to log into multiple accounts simultaneously.
3. Assessment of Attack Success:
– The final phase involves the attacker monitoring the attack’s success rate. They keep track of any accounts they successfully penetrate. These accessed accounts may then be exploited for further malicious activities, such as fraud or identity theft.
Business Impact of Credential Stuffing Attacks
The repercussions of successful credential stuffing attacks on businesses are profound and multifaceted:
– Data Breach: There’s a high risk of losing sensitive information, including personal and financial data.
– Operational Disruption: Business operations can be severely disrupted.
– Reputation Damage: The company’s reputation may suffer, leading to a loss of customer trust.
– Financial Loss: Customers may withdraw their business, leading to revenue loss.
– Increased Costs: Businesses often face heightened expenses related to incident response, informing affected customers, and providing credit monitoring services.
Key Points
- Enhanced Password Policy Enforcement
- Continuous Monitoring for Unusual Account Activity
- Regular User Education on Password Security
- Immediate Response Planning for Data Breaches
- Routine Analysis of External Security Threats
